|
DMT Excel File - People Page
This page is an index of the people matching Person A. It lists every Person C who matches Person A.
When comparing two files, this page is the second page of the produced Excel file, following the Chromosome Map page which is the first page.
When combining all results, this page is a separate Excel file for Person A and it is called the People file. This is the file that you update the MRCAs you know for Person A's relatives. See: Set Up Your People File and MRCAs. The People page and People file have exactly the same format.
The illustration below shows a combine all results People file that shows only the first 5 lines in each cluster.
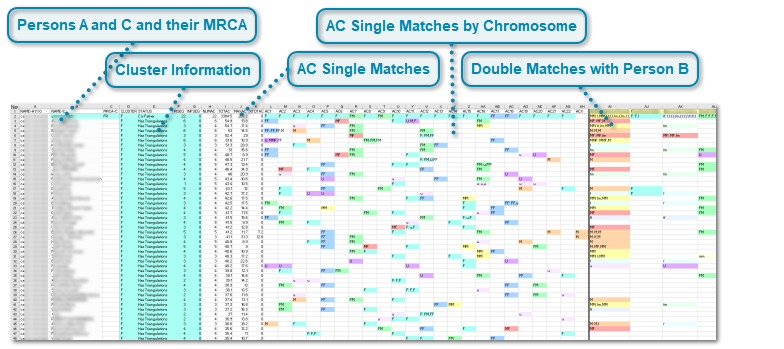
 Persons A and C and their MRCA
Column A (NAME-A) is the name of Person A. The column name in cell A1 will be NAME-A (1 X) if Person A is male, i.e. has 1 X chromosome, and it will be NAME-A (2 X) if Person A is female, i.e. has 2 X chromosomes. To change this value, use the Person A Sex dropdown on Double Match Triangulator's Main Window. Column B (NAME-C) are the names of all the C people who match Person A. Person C names beginning with ## have overlapping matches, which indicate there likely are two or more indistinguishable people having the same name. The ## warns you that their matches have been combined under that one name. Unless you know that all the people with ## have the same MRCA, you should not assign them an MRCA so that they will not improperly influence the ancestral path assignments.
Column C (MRCA-C) contains your entries of any Most Recent Common Ancestors (MRCA) for Person A and Person C that you know. See Set Up Your People File and MRCAs for more info on how to enter your MRCAs. If the MRCA has been entered, then columns B and C will be given a background shade based on what the MRCA is.
| |
 Cluster Information
Column D (CLUSTER) contains the cluster that DMT assigns to Person C. The Cluster is the ancestral path from Person A that is expected to lead to Person C. Clusters help classify the side of the family that each person may belong to. The people page is grouped by cluster. They will allow you to genealogically focus on that line to try to find how Person C is actually related to Person A. When you determine their actual relationship, then you can fill in this person's MRCA in column C of Person A's people file and run the whole shebang again.
The cluster will be calculated based on the most common agreed upon ancestral path on chromosomes 1 to 23. For example if a Person C has just two chromosomes with ancestral paths assigned of FF and FMF, then the cluster for Person C will be F.
 Cluster R is for people whose MRCA is R, meaning they share both parents with Person A, i.e. Person A's children, grandchildren, siblings, nephews and nieces.  Cluster U is for people whose parental side did not cannot be determined, or people whose chromosomes are equally represented with ancestral paths on both parents.  Cluster X is for people that only have excluded matches.
For people who have a known MRCA (with an R at the end), that MRCA will always be used as the cluster (less the trailing R).
The background shade of the cluster is based on the first two letters of the cluster. A darker shade is used if the person has triangulations and a lighter shade is used if not.
Column E (STATUS) indicates the nature of the matches between Persons A, B and C:
 or  indicates Person C is a parent of Person A. The MRCA of Person C must have been specified as FR or MR.  indicates that Person A, B and C triangulate on at least one segment. 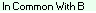 indicates that Person A and Person B both match Person C, but they do not triangulate anywhere. 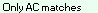 indicates that Person A matches Person C, but person B does not match Person C.
Column F (TRISEG) gives the total number of triangulating segments between Person A, any of the B people, and Person C.
Column G (INFSEG) gives the number of inferred segments that any of the B people have with Person C.
| |
 AC Single Matches
Columns H (NUMAC), I (TOTAC), J (MAXAC) and K (XTOTAC) give the number of segments matching between Person A and Person C, their total match length in cM, the largest matching segment length in cM, and the total match length on the X chromosome in cM.
Note that the TOTAC includes only segments that at least as large as the MinTriang segment limit that you have set. The default is 7 cM. Each company has their own limit as to what they include in their total, so their total cM may be different. TOTAC also excludes X chromosome segments.
Within clusters, the people on the Chromosome Map page are sorted by highest total match length (TOTAC) so that the presumably closer relatives of Person A in each cluster will be listed first.
BC Single Matches
When comparing two files with each other (Person A with Person B), there will be four additional columns included in the people file following the XTOTAC column:
NUMBC, TOTBC, MAXBC AND XTOTBC, which is the same information but for the matches of Person B with Person C rather than Person A with Person C.
| |
 AC Single Matches by Chromosome
The next 23 columns (L ... AH) show for every chromosome, the ancestral lines assigned to each match between Person A and Person C on that chromosome. Triangulations are in uppercase. Non-triangulations are in lower case. If the ancestral line is an unknown parent, then it is "U" or "u". Inferrals are shown as "i".
If there is more than one single match on the chromosome, a consensus ancestral path is determined and shown as the first path in the list followed by a colon. Triangulations take precedence in determining the ancestral path. Unknown parents and inferrals make no contribution to the consensus path.
e.g. 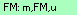 shows that there are three single A-C matches on the chromosome.The first A-C match has ancestral path m, which is non-triangulating on Person A's mother's side. The second A-C match is a triangulating FM match on Person A's father's mother's side. The third match is a u unknown parent match. In this example, the consensus is the triangulating FM match, so the consensus FM: is added before the other three. The background shade is based on the consensus match.
| |
 Double Matches with Person B
These are only included when combining all files. One column is added for every Person B that was used. Person B's name is listed in row 2. These columns will give you information about which C people are triangulating or otherwise interacting or not interacting with each B person.
Under each B person's name are the ancestral paths of matches between Person A and Person C that overlap with a match of Person B and Person C, or overlap with a match of Person A and Person B. Where there is more than one ancestral path, a consensus ancestral path is determined and shown as the first path in the list followed by a colon. The consensus ancestral path is determined the same as described in AC Single Matches by Chromosome above. The background shade is based on the consensus match.
Since these are double matches, they will triangulate and be shown in uppercase if the third leg (A-B or B-C) also matches on the segment. If the third leg does not match on the segment, they will not triangulate and will be shown in lowercase.
| |
|
|