|
DMT Excel File - Chromosome Map Page
When comparing two files the output of the DMT program is an Excel file that has two pages. The first page is the Chromosome Map page and shows all Chromosomes 1 to 23 on the page, one after another.
When combining all files the output of the DMT program includes 23 Excel files, with one Chromosome Map page for each chromosome.
The two Chromosome Map pages are very similar and both are described here. The example shown below is from Chromosome 1 when combining all files.
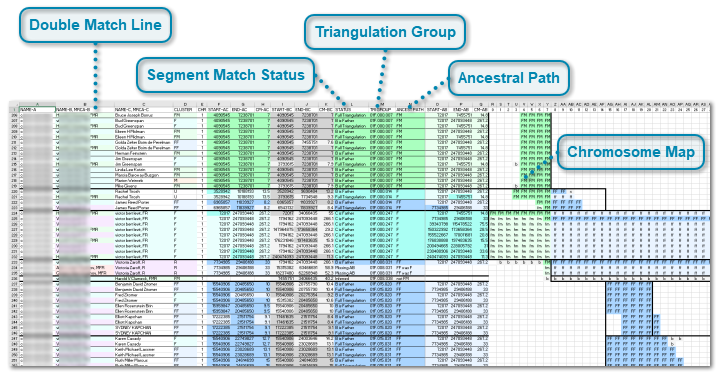
 Double Match Line
Column A (NAME-A) is Person A, the person you are interested in whose ancestors you want to find. Column A is not shown for inferred matches to indicate that Person A does not match.
Column B (NAME-B, MRCA-B) is Person B, the person whose segment match file is compared and double matched with Person A. If Person B has a MRCA, the MRCA is shown following the name and a comma. The background shade is based on the MRCA. Person B is not shown for A-C matches or Missing B-C matches to indicate that Person B does not match.
Column C (NAME-C, MRCA-C) is Person C, who is always one of the people who Person A matches. Only people Person A matches to are included in Person A's analysis. If Person C has an MRCA, the MRCA is shown following the name and a comma. The background shade is based on the MRCA.
Column D (CLUSTER) is the cluster that was determined for Person C. It is determined from the most common ancestral line of the segment matches between Person A and Person C. See the People Page for more information about the cluster. The background shade is based on the cluster.
Column E (CHR) is the chromosome the match is on. When comparing two files, all chromosomes are shown in order in the one file. Chromsome X is included last. When combining all files, each chromosome is in their own file.
Columns F (START-AC) and G (END-AC) give the start and end base addresses of the Person A match with Person C. The background shade is based on the ancestral path in column N. It is a darker shade if the address coincides with the start or end of the triangulating region. The AC matches are what you see in a chromosome browser from Person A's point of view.
Column H (CM-AC) gives the number of Centimorgans (cM) of the match between Person A and Person C. The background shade is that same as for Columns F and G. It is a darker shade if START-AC and END-AC both coincide with the start and end of the triangulating region, meaning it is also the length of the triangulation.
Columns I (START-BC) and J (END-BC) give the start and end base addresses of the Person B match with Person C. They are shown in a background shade of grey to illustrate that this is not a Person A match. It is a darker shade if the the address coincides with the start or end of the triangulating region.
Column K (CM-BC) gives the number of centimorgans (cM) of the match between Person B and Person C. The background shade is grey. It is a darker shade if START-BC and END-BC both coincide with the start and end of the triangulating region. meaning it is also the length of the triangulation.This value can help identify whether Person A or Person B is related more closely to the C person. In general, close relationships will have longer BC matches than more distant relationships. Also, BC matches that are longer than the AC match indicate a possible closer relationship of B to C than of A to C. Shorter matches indicate a possible farther relationship. This may provide clues as to the relationship between Persons A, B and C and who their common ancestor might be.
Column L (STATUS) is described in its own section below: Segment Match Status
Column M (TRIGROUP) is described in its own section below: Triangulation Group
Column N (ANCEST PATH) is described in its own section below: Ancestral Path
Columns O (START-AB) and P (END-AB) give the start and end base addresses of the Person A match with Person B. The background shade is based on the ancestral path in column N. It is a darker shade if the address coincides with the start or end of the triangulating region. Triangulations can only occur where A matches B. The "Freeze Pages" property is set to Column N, so scrolling right will hide columns O, P and Q.
Column Q (CM-AB) gives the number of centimorgans (cM) of the match between Person A and Person B. The background shade is that same as for Columns O and P. It is a darker shade if START-AC and END-AC both coincide with the start and end of the triangulating region, meaning it is also the length of the triangulation.
| |
 Segment Match Status
These are the possible status values for each segment match:
 Full Triangulation Full Triangulation means that Person A matches Person C, Person B matches Person C, and Person A matches Person B on at least some part of this segment.Triangulations often indicate that the segment may have come from a common ancestor. The tricky part for you is to genealogically figure out who that ancestor was. In the Chromosome Map area of this page, the triangulating segments are denoted with capital letters and a dark shaded background.
 These are full triangulations where the parent of the MRCA of A-B differs from the parent of the MRCA of A-C. Because the parents differ, the MRCAs are not likely the same and there may be a triangulation only because A-B, A-C and B-C are each matching on differing parents, i.e. opposite chromosomes. DMT treats these like Single A-C matches (see below). For more information about this situation, see my blog post: Triangulation does NOT mean IBD. If there are any MRCAs that differ, then the number of them is given in the log file to alert you, and you can use the Excel "find" to search for them in the Status column.
 or B is Mother or C is Father or C is Mother indicates that Person A is matching their parent on the segment and that Person A and their parent are triangulating on that segment with the other person. This is a full triangulation but it is special because the parent effectively "phases" the match to that parent's chromosome. If the parent's match is smaller than Person A's match, then the extra bits of the A-C match are marked as false and will be shown with 
 A Missing B-C Match is where Person A matches Person C and Person A matches Person B, but Person B does not match Person C on this segment. Person B and Person C must be in-common-with each other, i.e. they must match somewhere, but not here. These matches are very useful, because if they in fact are not a triangulation, then they cannot occur on the same parental chromosome as any triangulations that are at that location. They would then have to be A-C matches that are on the other parent's chromosome. Thus, even though a Person B may be related on one parent's side, information is available for both parents' chromosomes.
 A Missing A-B Match is where Person A matches Person C and Person B matches Person C, i.e. a double match, but Person A does not match Person B on the segment so it is not a triangulation. This works the same as a Missing B-C match.
 An Inferred match is where Person B matches Person C but Person A does not match Person C on the same segment. When the MRCA of Person A with both Person B and Person C are known, in some cases the B-C match may be able to tell you what the A-C match cannot be. Inferred matches are shown in a grey shade because to indicate that they are not an A-C match. The ancestral path of an inferred match will always start with "not ", e.g.  . The ancestral path that this match refutes is the one given.
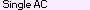 A Single A-C match is an A-C match that does not triangulate, is also not a missing B-C or missing A-B match, and is at least as large as the Min Single cM limit. Being larger than the Min Single limit assumes that this match is large enough to not be a match by chance and likely was passed down from a common ancestor. If the MRCA for person C was assigned, then the MRCA's parental side will be used, unless there are also overlapping triangulations on that parental side which indicate a conflict. If the MRCA is not assigned and there were triangulations on that segment then the segment will be assigned to the opposite parent. In case of a conflict or no MRCA and no triangulations, then this match is placed into the "U" unknown parent section.
MRCA Bad on X - if you see this status, then you may have a Person C matching on the X chromosome whose MRCA is on Person A's father and Person A is male. That can't happen since a male only receives an X chromosome from his mother. DMT only includes a mother-side X chromosome when Person A is male. Or you may have a Person C matching on the X chromosome whose MRCA includes "FF". That can't happen because an X chromosome doesn't pass down from a male to a male.
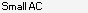 A Small A-C match is a single match that does does not reach the Min Single cM limit. These matches might be by chance matches that do not come from a common ancestor. They are included in DMT's output so that you can still see all of Person A's matches, but they are put into the "X" excluded section so that you will know what A-C segments were not used in the analysis.
 A Small Inferred match is an inferred match that does does not reach the Min Single cM limit. These matches might be by chance B-C matches that do not come from a common ancestor of B and C. They are included in DMT's output so that you can still see all the inferred matches, but they are put into the "X" excluded section so that you will know what inferred segments were not used in the analysis.
| |
 Triangulation Group
The triangulation group containing the segment is specified with an 11 character notation based on a similar notation designed by Jim Bartlett.
The first two characters is the chromosome number, "01" to "23", where "23" represents the X chromosome.
The 3rd character is either "F" for father's chromosome, "M" for mother's chromosome, "U" for unknown whether father or mother, or "X" for exclude from analysis. The latter group is used for small single segments and small inferred segments.
Then are two sets of 3 digit numbers with a period separating them for readability. The 3 digit numbers are the starting and ending base positions of the triangulation group given in Mbp (mega base pairs = 1,000,000 of them). They are truncated to the nearest Mbp which is good enough for accuracy since there is usually extra matching at the ends of each segment.
DMT bases the start and end of of triangulation groups on the positions where triangulations start and end. Each segment will be assigned to the smallest triangulation group that contains the segment.
In the "U" unknown parent section and "X" excluded section, only one group is used on each chromosome with the start and end positions covering the entire chromosome.
For example, 01F.003.007 refers to the triangulation group that is on father's chromosome 1, starts at a base address of 3 Mbp and goes up to and includes the 9 Mbp column, i.e. 10 Mbp starts a new triangulation group.
| |
 Ancestral Path
The ancestral path is determined where possible for each segment match. MRCAs are needed to calculate ancestral paths, and the notations of the two are similar.
Ancestral paths are comprised of "F" and "M" characters, so an FMF ancestral path states that the segment may come from Person A's father's mother's father. Ancestral paths never contain the trailing "R" that MRCAs do.
The ancestral path of a segment is based on the agreed-upon ancestral path at all the Mbps between the segment's start position to its end position. If, for example, part of a segment is FMF and another part is FMM, then the consensus is taken to be FM.
 - The ancestral path of an inferred segment is specified with the word "not" before the path, because an inferred path tells you the path that likely is not the correct one.
 - For a combined run, if the combined run results in a different ancestral path than the A versus B run it came from, then the ancestral path from the A versus B run is shown following the word "was".
 - If a segment triangulates, but Person C does not have an MRCA and there are overlapping triangulations on both parents, then the parental side of this segment cannot be determined. The ancestral path is assigned "both" and the segment is placed in the U unknown parent section.
 - If a segment triangulates, but Person C does not have an MRCA and there are not any overlapping triangulations on either parents, then the parental side of this segment cannot be determined. The ancestral path is left blank and the segment is placed in the U unknown parent section.
 For a combined run, If both parents have tested and an A-C segment match does not match either parent, then the ancestral path is assigned "No Parent" and the segment is placed in the U unknown parent section.
| |
 Chromosome Map
The right section of the Chromosome Map page in the Excel file, from columns O to JB, provides a simple visual representation of the matches.
The numbers at the top (Row 1) represent the base pair addresses in millions (Mbp).
So, for example, 14 would represent base pair addresses between 14000000 and 14999999.
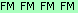 - Capital letters with dark shaded backgrounds represent triangulations. The capital letters indicate the ancestral path up to the grandparent that was determined for each Mbp. So the possibilities are F, FF, FM, M, MF, MM. The color used is based on the parent or grandparent. You can also have triangulations where the parental side is unknown. 
 - Small letters with light shaded backgrounds are segment matches which are not triangulations The letters also indicated the ancestral path up to the grandparent, but there may also be  for B-C matches of inferrals or extra B-C matching before or after the A-C match starts and ends, e.g: 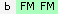 . You can have matches that are not triangulations where the parent is unknown 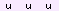 , and matches that are excluded from analysis: 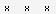
The dark vertical and horizontal lines separate triangulation groups.
Some segments may seem to span two ancestral lines, such as the segments shown here that start as FM and end as FF:
Technically, ancestors can change over one segment but they should not normally change grandparents. DMT extends grandparents to triangulation group boundaries so within a triangulation, if grandparents change then it will be at a triangulation boundary.
| |
|
|